PRP Troubleshooting Overview
PRP is a achieves failsafe operation in power substation networks by duplicating the information. Zeus provides all the required passive and active testing functionality required to troubleshoot PRP including PTP, GOOSE and SV operating over PRP.
BARCELONA DEC/2025
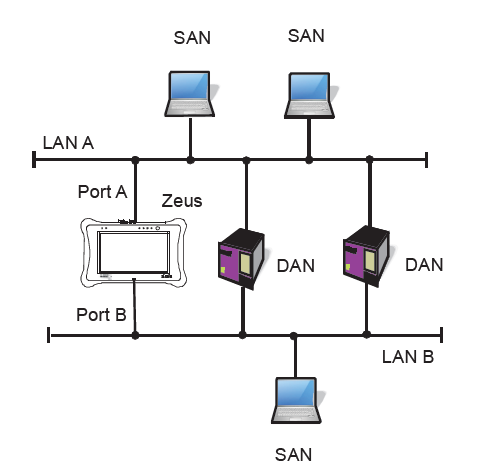
The Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP) provides failsafe operation in a LAN by duplicating the transmission media so that they work in parallel. Every piece of information is transmitted twice over mutually isolated networks (LAN A and LAN B). If one of the replicas is lost, it is very likely that the the information is still received through the alternative channel. In normal operation conditions, frames are received twice and Doubly Attached Nodes (DANs) implement a duplication detection algorithm designed to drop most duplicated frames before they are processed by higher protocol layers.
The PRP standard is flexible enough to accept interoperability with nodes connected to only LAN A or LAN B. These are called Singly Attached Nodes (SANs). There are not strict requirements for LAN A and LAN B. These are typically bridged Ethernet networks designed so that a failure in one of them does not affect to the second network.
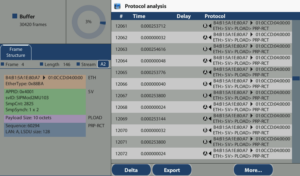
SV protocol capture in a PRP network
Despite its conceptual simplicity, PRP is a quite tricky technology that requires careful assessment. Some issues are hidden behind redundancy and they are only evident in faulty conditions. There are also some special features of PRP that require special attention: LAN A and LAN B ports in a DAN share the same MAC and IP addresses. They must never be attached to the same PRP LAN. DANs must generate special data flows to report the kind of node they are.
They also need to discard duplicated frames. It is not mandatory that all duplicates are detected and dropped but it is still expected that most duplicates will be correctly processed. Moreover, DANs must keep a table with other DANs attached to the network in order to detect of duplicates. For PTP there are also specific requirements and standard IEC 61850-9-3, the PTP Utility profile, specifies a special version of the Best Master Clock Algorithm (BMCA) for PTP over PRP. These and other conditions are potential sources for faults or service degradation and they can only be prevented or corrected through specialized testing.