GPS Set up in xGenius
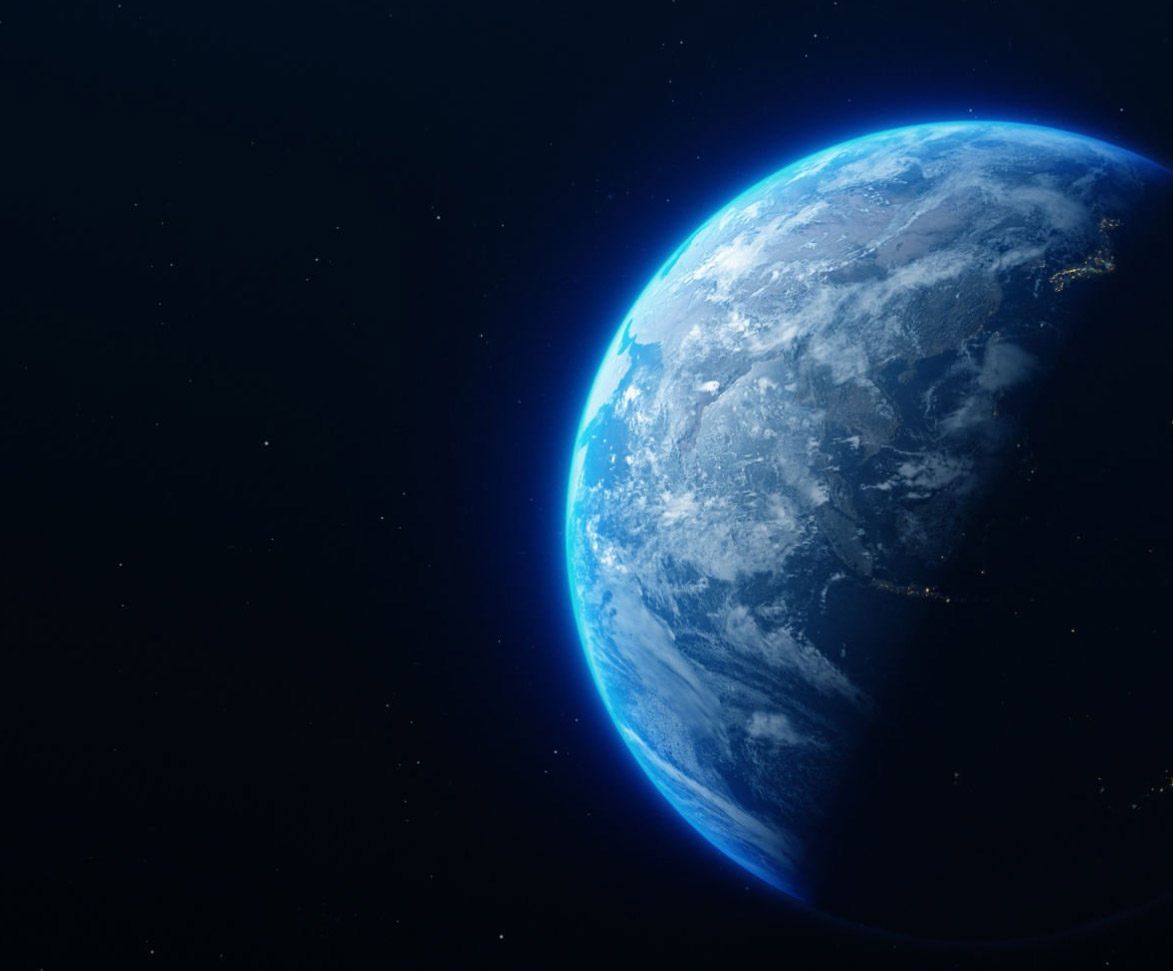
GNSS is not only critical for verifying the accuracy of protocols such as PTP, SyncE, IRIG-B, 1PPS or NTP, but it is also required for one-way delay (OWD) measurements with two testers and for generating transmission and timing protocols.
BARCELONA NOV.17.2023
GNSS synchronization
GPS synchronization is primarily concerned with maintaining precise timing and frequency alignment across different network elements. This is essential for the efficient and reliable operation of telecommunications. Then, in the context of testing, GPS is often critical for performing certain tests to verify the frequency and timing accuracy of signals such as PTP or NTP. GNSS is also required for one-way delay measurements using two testers that must be precisely synchronized to a common time reference. GNSS may also be required when generating certain timing protocols, as it is fundamental to maintaining the integrity of the transmitted signals, reducing jitter and ensuring accurate data transmission.
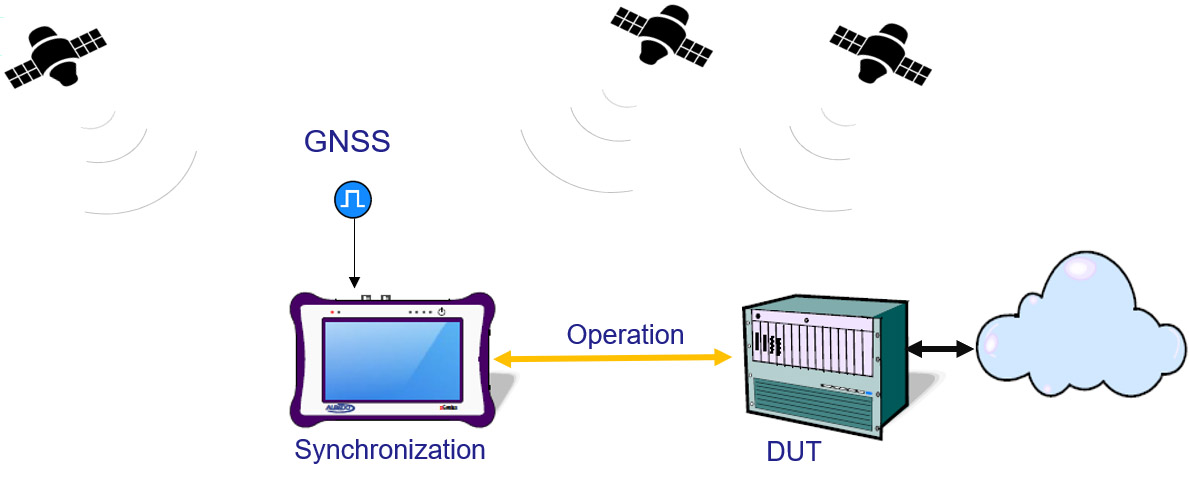
Fig 1. ALBEDO testers are eqipped with a built-in GNSS receiver.
Built in GNSS receiver
xGenius / Zeus units can optionally be equipped with a built-in GNSS receiver, which is supplied with a compact antenna with 5 m of coaxial cable plus 10 m of extension cable connected to an SMA connector. It is possible to use another antenna as long as the specifications of the GNSS module are respected.
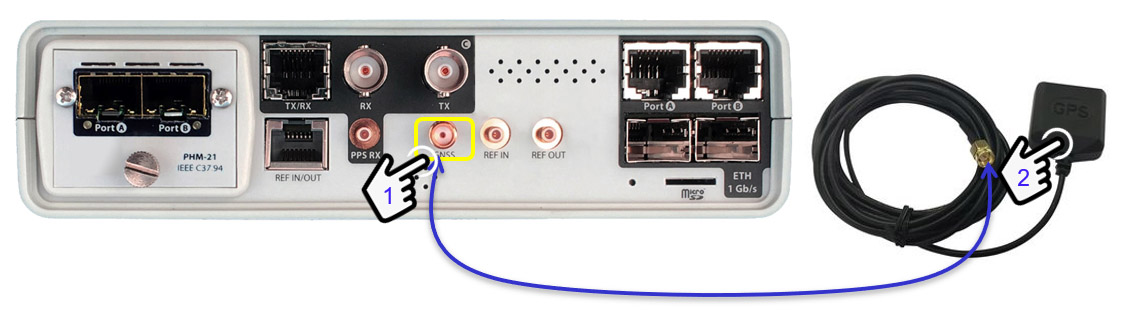
Fig 2. Connecting the GPS antenna.
The GNSS interface can be used to synchronize the system time to a satellite constellation, but for certain test units, some results may be dependent on the GNSS timing source. In this case, the test application can enable GNSS reception on its own. In either case, the GNSS status can be verified using the same Clock Reference.
Holdover Mode
Holdover mode is useful when the GNSS clock reference is lost for some reason or could not be used at the test site. xGenius / Zeus units with OCXO and Rubidium oscillators can operate in holdover mode when this circumstance occurs because it is necessary to maintain accurate frequency and phase for a period of time required during testing, which can range from a few minutes for OCXO units to a few hours for Rubidium units.
Fig 3. The GNSS receiver is a common accessory of ALBEDO testers.
The results will be accurate for a period of time as long as the test unit is not restarted.
xGenius & Zeus
xGenius and Zeus provide in-depth insight into the design, installation, maintenance, troubleshooting and engineering of Smart Grid communications infrastructures. The instrument can test Ethernet/IP, PTP, GbE, IRIG-B, T1/E1, G703, C37.94 and GOOSE, SV and MMS protocols. One-way delay testing, supported by GPS, is available on all interfaces. Zeus has a set of programmable filters to capture live traffic at wire speed. You can now analyze GOOSE, SV, MMS and other protocols to decode and store them in PCAP format or calculate propagation delay from local or remote substations.
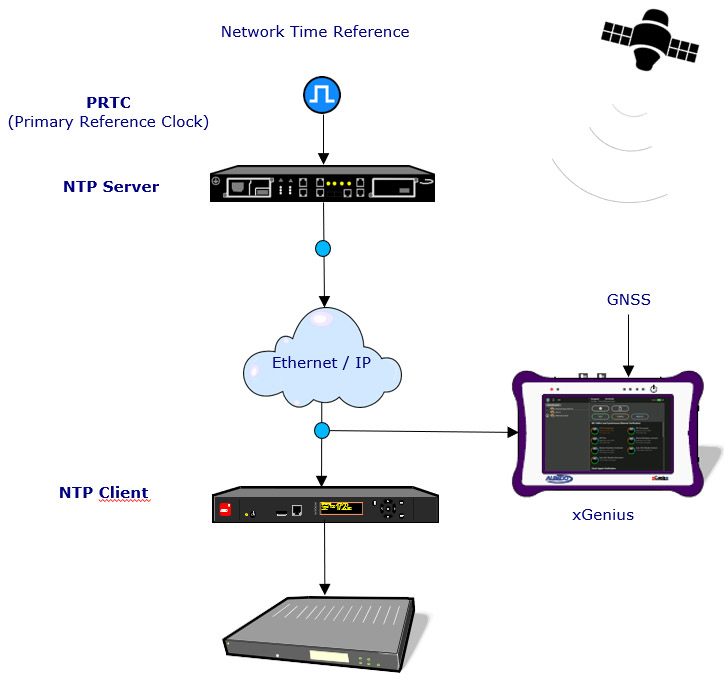
Fig 4. xGenius disciplined to the GPS and verifying the NTP protocol.
The built-in GNSS receiver is a hardware option you have to purchase for your testers and it is supplied with a compact antenna with 5 m of coaxial cable plus a 10 m extension cable.


